A Complete Guide To Design Patterns In Kotlin: Proxy Design Pattern
Tutorial on how to implement the proxy design pattern with Kotlin
Filter by Category
Filter by Author

Tutorial on how to implement the proxy design pattern with Kotlin
Posted by Baraa Abuzaid

Tutorial on composite design pattern with code example In Kotlin
Posted by Baraa Abuzaid

Here we'll implement a draggable map with a fixed marker on top. that's only change when moving the map just like UBER.
Posted by Baraa Abuzaid

Get up and running with Kotlin in no time
Posted by Baraa Abuzaid

Discussing Kotlin Interface delegation and the shortcoming of the implementation inheritance
Posted by Baraa Abuzaid

The adapter design pattern is a structural design pattern that's very useful when maintaining a legacy code or adding a new features.
Posted by Baraa Abuzaid

The Façade design pattern is a structural design pattern. It reduces coupling and improves code readability.
Posted by Baraa Abuzaid

Will be going through the Creational Design Pattern illustrating how and where to use it.
Posted by Baraa Abuzaid

This tutorial will explain the fundamentals of ViewModel and LiveData and how to use them by creating simple demo App that shows recent movies.
Posted by Baraa Abuzaid

This is a brief look into MVP clean architecture discussing why it is the best architecture for android development
Posted by Baraa Abuzaid

Tutorial on how to implement the proxy design pattern with Kotlin
A Proxy design pattern is a structural design pattern. the idea behind is to make a proxy object that is capable of performing tasks similar to the original object. The need for using proxy class could vary but we could depict the following main scenarios.
Virtual proxy this is when using a proxy class as an alternative for a real class because the real class is a resource-intensive to instantiate. for example, the videos in the video edit software, where the program wouldn’t load the video with actual size and resolution because it might be huge. Instead it loads a proxy object (video) a light weight version that’ll easy editing.
Protection Proxy this one is when using proxy class for authority and access control. You might have already notice that in some website, you are able to browse through and add stuff to your cart or wishlist but when you need to post a review or buy somthing It goes along and ask you to login. In this case a proxy object have been in place of real object. Then when you are about to perform more sophisticate actions. A proxy class authenticate you then load or redirect the call to a real object.
Remote proxy this one when the proxy class is local and real object is remote and exists somewhere else.

Proxy Pattern in UML class diagram
Let’s have a more concrete example, suppose we have shipping company like DHL or FedEx. The shipments arrive airport before it been dispatched to the nearest sorting facilities. With that, we need a mechanism in place to only send parcels to facility that is close to the parcel final destination and ensure that the destination facility is actually not full.
To implement a system like that using Proxy pattern. First, will define our interface. IShipment interface in this example it is only going to have one method which dispatchParcel().
Second, will make a proxy class (ParcelDispatcher) and a real subject class(SortingFacility). both are implementing IShipment interface. Below is UML class representation.
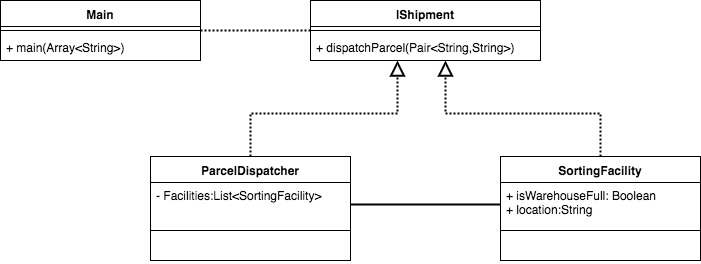
Proxy Pattern Example In UML Class Diagram
Let us see how this will translate to code
interface IShipment {
// the parcel is represented by a pair
// where first String is parcel content second is parcel location
// (content to location )
fun dispatchParcel(parcel:Pair<String,String>)
}
class SortingFacility(val location:String,var isWarehouseFull:Boolean) : IShipment{
override fun dispatchParcel(parcel: Pair<String, String>) {
println("${location} facility doing dispatching business...")
}
}
class ParcelDispatcher : IShipment {
// for the seek of simplicity I'll just represent the location
// with a simple string.
private var facility = listOf<SortingFacility>(
SortingFacility("North",true),
SortingFacility("North West",false),
SortingFacility("South",false),
SortingFacility("West",true),
SortingFacility("East",false)
)
override fun dispatchParcel(parcel: Pair<String, String>) {
val facilityNearTpParcelLocation = facility.filter { it.location.contains(parcel.second,true) && !it.isWarehouseFull }.first()
facilityNearTpParcelLocation.dispatchParcel(parcel)
}
}
fun main(args:Array<String>){
var parcel = "SmartPhone" to "North"
var parcelDispatcher = ParcelDispatcher()
parcelDispatcher.dispatchParcel(parcel)
}
Featured Photo by Atik sulianami

Understanding UML Diagram might be quite daunting task especially for those of Us whose not coming from formal CS background, you see all of these square boxes and different type...

This is a follow up to my last tutorial Understanding UML Class Diagram so if you missed it please check it out first. Here will be going through a problem statement and try to...